RF power amplifier
An RF power amplifier is a type of electronic amplifier used to convert a low-power radio-frequency signal into a larger signal of significant power, typically for driving the antenna of a transmitter. It is usually optimized to have high efficiency, high output Power(P1dB) compression, good return loss on the input and output, good gain, and optimum heat dissipation.
Applications
The basic applications of the RF power amplifier include driving to another high power source, driving a transmitting antenna, microwave heating, and exciting resonant cavity structures. Among these applications, driving transmitter antennas is most well known. The transmitter–receivers are used not only for voice and data communication but also for weather sensing (in the form of a RADAR). Microwave or RF heating is an industrial application which is also benefiting our homes in the form of microwave ovens. Exciting cavity resonators is quite a research lab and industrial application of an RF source. Particle accelerators utilize RF sources extensively.
Wideband amplifier design
Impedance transformations over large bandwidth are difficult to realize, thus most wideband amplifiers use 50 Ω output loading. Transistor output power is then limited to
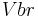 is defined as the breakdown voltage
is defined as the breakdown voltage
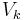 is defined as the knee voltage
is defined as the knee voltage
and